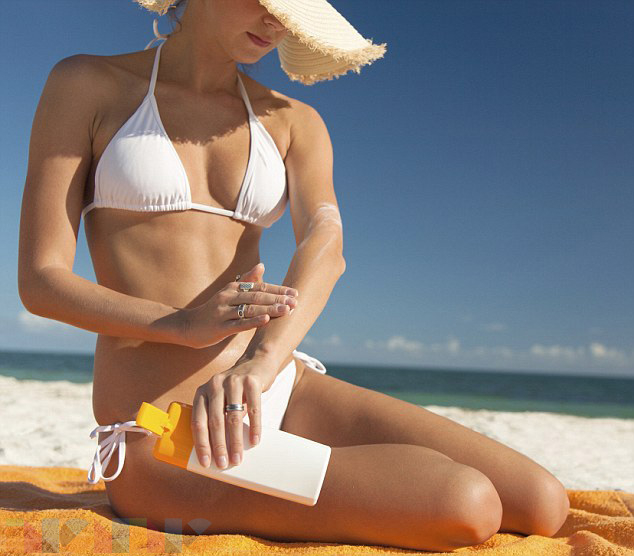
Medical experts are warning about a surge of misinformation regarding sunscreen, with some social media posts even advising against its use. Experts emphasize that sunscreen is essential for protecting against skin cancer. NBC News' Anne Thompson reports.
Sun Safety Under Siege: Debunking Sunscreen Misinformation.
The summer sun beckons with warm days and long evenings, but with it comes the ever-present need for sun protection. However, amidst the beach umbrellas and SPF labels, a concerning trend is emerging: the spread of misinformation about sunscreen. Medical professionals are urging caution, highlighting the dangers of these false claims and the importance of sun safety.
Here's a breakdown of some common sunscreen myths and the science-backed truths that dispel them:
Myth 1: Sunscreen Blocks Vitamin D Production – Busted! Sunscreen does filter ultraviolet (UV) rays, but it doesn't completely block vitamin D synthesis. Our bodies naturally produce vitamin D from sunlight exposure, but a moderate amount (around 10-15 minutes) is sufficient. Sunscreen allows for this while preventing sunburn and premature ageing.
Myth 2: Sunscreen is Full of Chemicals – Not Necessarily! Sunscreens contain ingredients that absorb or reflect UV rays. While some are chemical (like oxybenzone), others are physical blockers (like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide). Both types can be effective, and choosing a mineral-based option is a good alternative for those concerned about chemicals.
Myth 3: Sunscreen Causes Cancer – Absolutely False! There is no scientific evidence to support this claim. In fact, the opposite is true. Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States, and sun exposure is a major risk factor. Sunscreen significantly reduces this risk.
Myth 4: A Tan is a Sign of Health – Not Quite! A tan is actually the body's defense mechanism against UV damage. It's a sign of sunburned skin cells producing melanin, a pigment that tries to shield deeper layers. A healthy tan simply doesn't exist.
Myth 5: Only Need Sunscreen on Sunny Days – Wrong! UV rays are present even on cloudy days. Up to 80% of the sun's UV rays can penetrate clouds, meaning you still need protection.
Myth 6: Higher SPF Means More Protection – Mostly True! Sun Protection Factor (SPF) indicates a sunscreen's ability to block UVB rays, the ones that cause sunburn. SPF 30 blocks 97% of UVB rays, while SPF 50 blocks 98%. While SPF 50 offers slightly more protection, the difference is marginal. Choosing SPF 30 is a good starting point, with SPF 50 recommended for extended sun exposure or those with fairer skin.
Myth 7: Waterproof Sunscreen Lasts All Day – Not Exactly! Water-resistant sunscreens do offer some protection after swimming or sweating, but they need to be reapplied every two hours, or more often if you're toweling off or sweating heavily.
Myth 8: Sunscreen Makes Vitamin D Deficiencies More Common – Not True! Vitamin D deficiency is a complex issue with various contributing factors. While sunscreen may slightly reduce vitamin D synthesis, a balanced diet and moderate sun exposure can address this concern.
Myth 9: Sunscreen Causes Coral Reef Damage – Some Ingredients Can! Oxybenzone and octinoxate, found in some chemical sunscreens, have been linked to coral bleaching. Opting for mineral-based, reef-safe sunscreens is a better choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
Myth 10: Sunscreen is Unnecessary for Darker Skin Tones – Absolutely False! Skin cancer can affect people of all skin tones. While melanin offers some natural protection, it's not enough to completely shield against UV damage. Sunscreen use is crucial for everyone, regardless of skin color.
By understanding these myths and embracing sun safety practices, we can enjoy the outdoors while protecting our skin. Remember, sunscreen is an essential tool in your sun protection arsenal. Don't let misinformation cloud your judgment. Slip, slop, slap – and enjoy the sunshine responsibly!






 Ingning
Ingning







